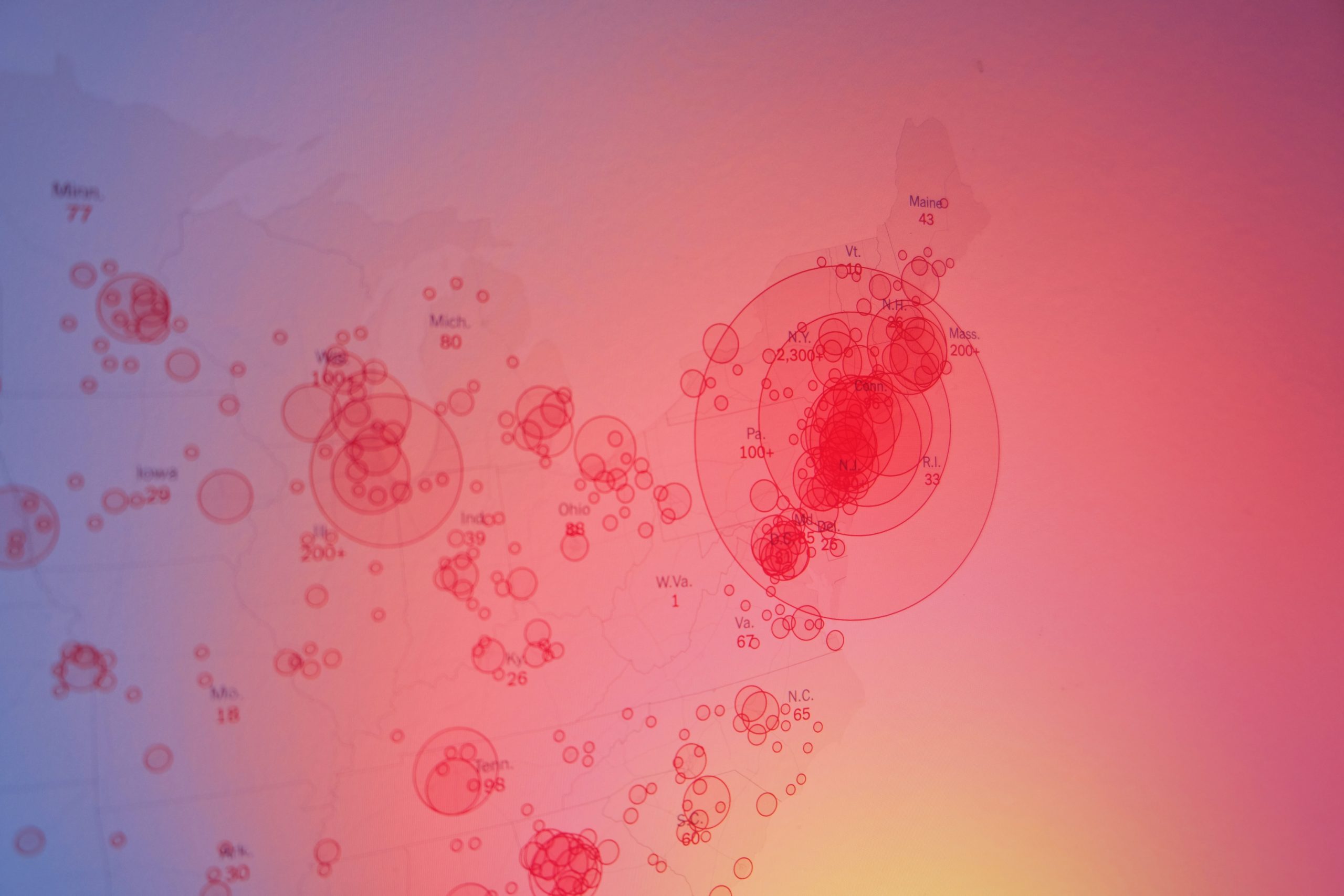

Princeton researchers map rural U.S. counties most vulnerable to COVID-19
April 15, 2020 ・ Morgan KellyA county-by-county analysis of the United States by Princeton University researchers suggests that rural counties with high populations of people over 60 and limited access to health care facilities could eventually be among the hardest hit by the coronavirus pandemic…
Climate change could make RSV respiratory infection outbreaks less severe, more common
December 16, 2019 ・ Morgan KellyOne of the first studies to examine the effect of climate change on diseases such as influenza that are transmitted directly from person to person has found that higher temperatures and increased rainfall could make outbreaks less severe but more…
Antibiotic resistance in food animals nearly tripled since 2000
October 9, 2019 ・ Morgan KellyThe growing appetite for animal protein in developing countries has resulted in a smorgasbord of antibiotic consumption for livestock that has nearly tripled the occurrence of antibiotic resistance in disease-causing bacteria easily transmitted from animals to humans, according to a…
Government subsidies could be key to containing hospital-born infections
April 3, 2019 ・ Morgan KellyHealth care-associated infections — illnesses that people contract while being treated in a hospital or other health care facility — sicken millions of people each year and cost billions of dollars in additional treatment. While there has been some improvement…


Urban Population, Transportation Patterns Affect How Flu Epidemics Play Out
October 8, 2018 ・ Morgan KellyThe more people a city has and the more organized its residents’ movement patterns, the longer its flu season is apt to last, new research co-authored by Princeton University researchers shows. Published in the journal Science, the findings are an important step toward predicting…


As antibiotics fail, global consumption of antibiotics skyrockets, further driving drug resistance
March 26, 2018Despite the threat of a global health crisis in antibiotic resistance, worldwide use of antibiotics soared 39 percent between 2000 and 2015.
Competing for blood: How ecologists are solving infectious disease mysteries
February 12, 2018 ・ Liz Fuller-WrightPrinceton ecologists found that co-infections of malaria and hookworm center on fights over a shared resource: red blood cells.
Undergrads exhibit semester research for “Disease Ecology, Economics and Policy”
December 19, 2017Students in the course “Disease Ecology, Economics and Policy” gathered in the Guyot Atrium Dec. 14 to present their semester research projects on the emergence and spread of disease.
To Predict How Climate Change Will Affect Disease, Researchers Must Fuse Climate Science and Biology
September 18, 2017To predict how climate change will affect disease, researchers need new statistical models that incorporate both climate factors and the climate-disease relationship, and account for uncertainties in both.



